Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. * denotes the co-first author.
2026
2025
- ISBI 2025
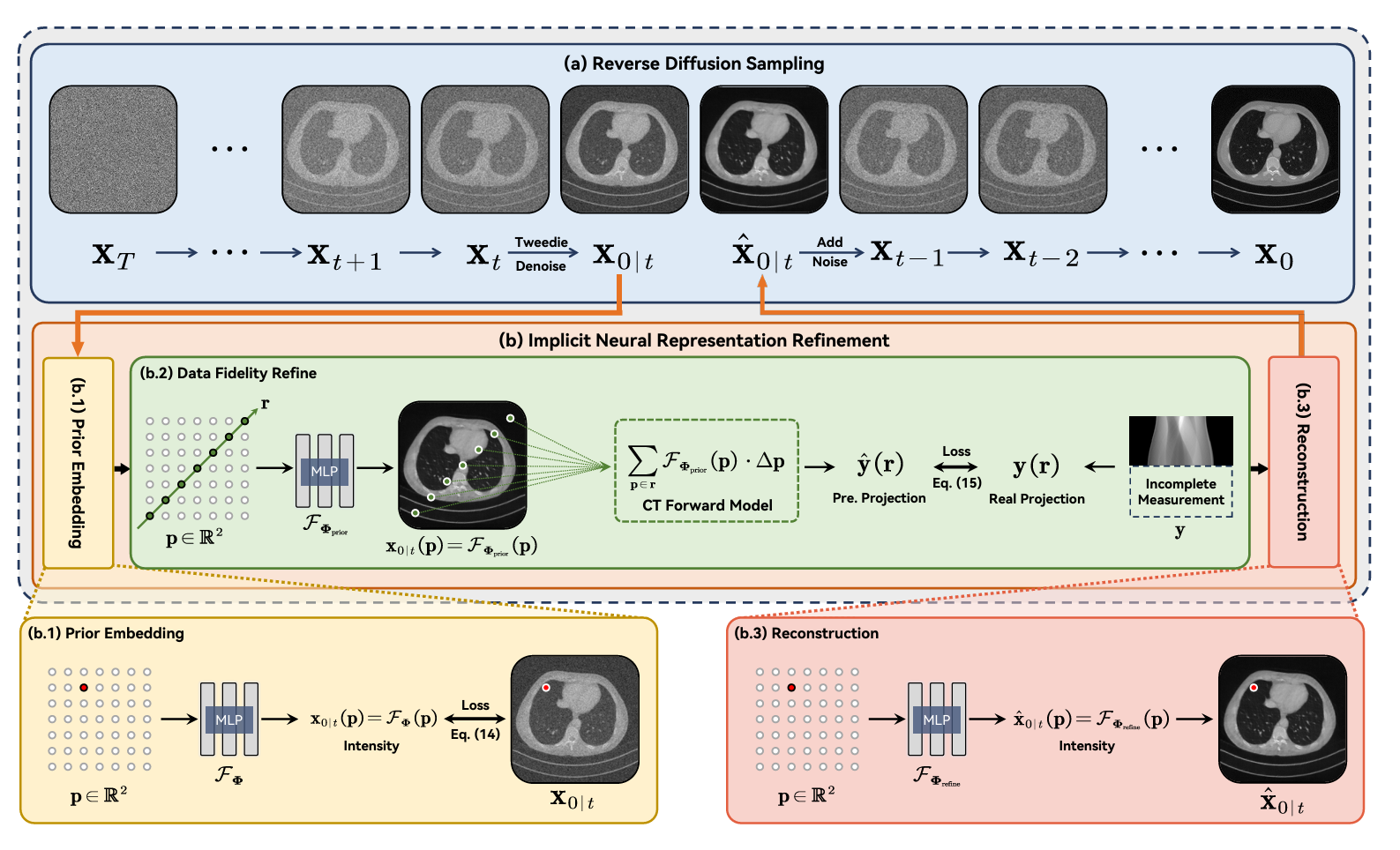
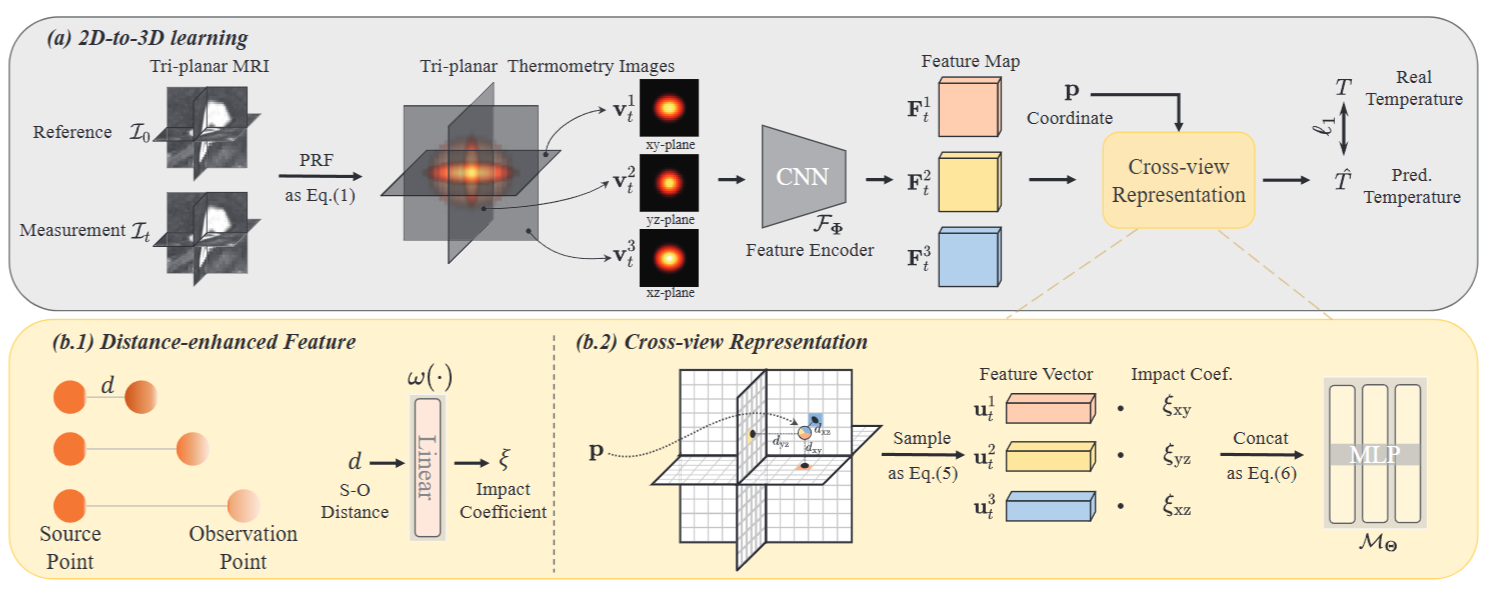 ×Accelerated 3D Thermometry Field Reconstruction from Tri-Planar Images via Cross-View Implicit RepresentationIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
×Accelerated 3D Thermometry Field Reconstruction from Tri-Planar Images via Cross-View Implicit RepresentationIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025 - ISBI 2025
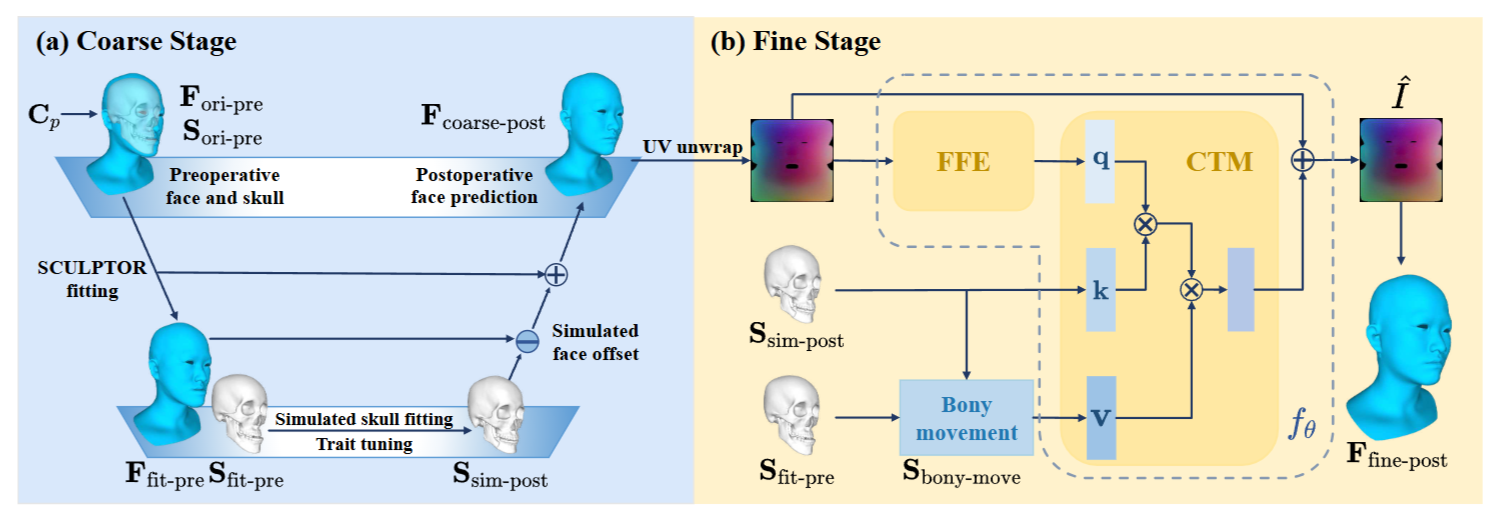 ×Blending Parametric Model and Neural Refinement: A Coarse-to-Fine Approach for Predicting Facial Changes in Orthognathic SurgeryIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025
×Blending Parametric Model and Neural Refinement: A Coarse-to-Fine Approach for Predicting Facial Changes in Orthognathic SurgeryIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2025 - BSPC 2025
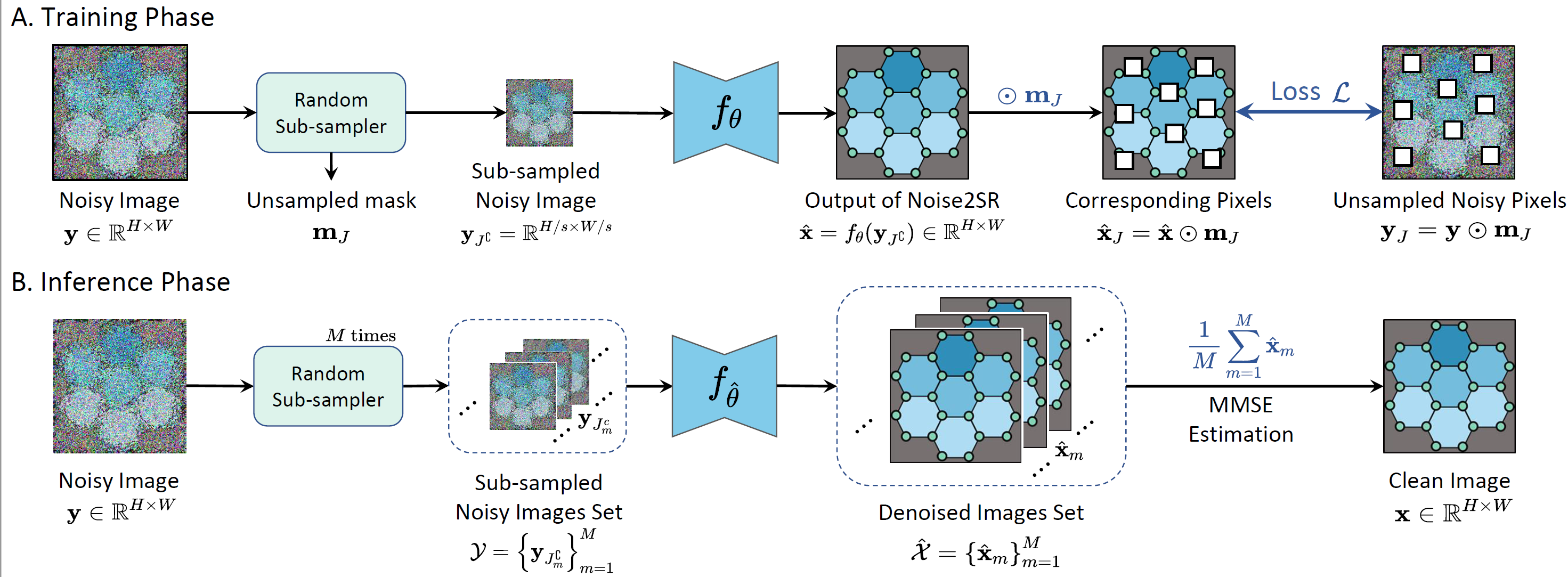
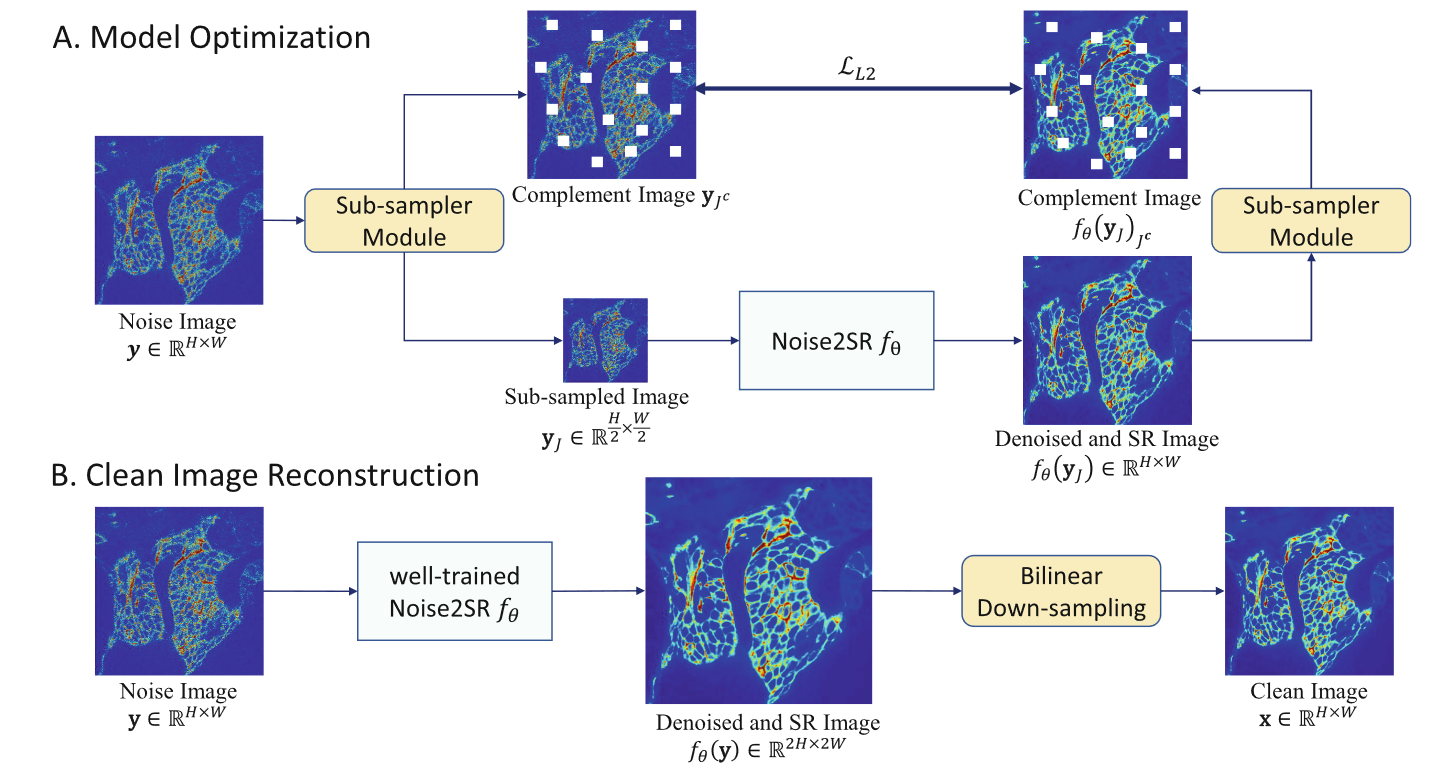
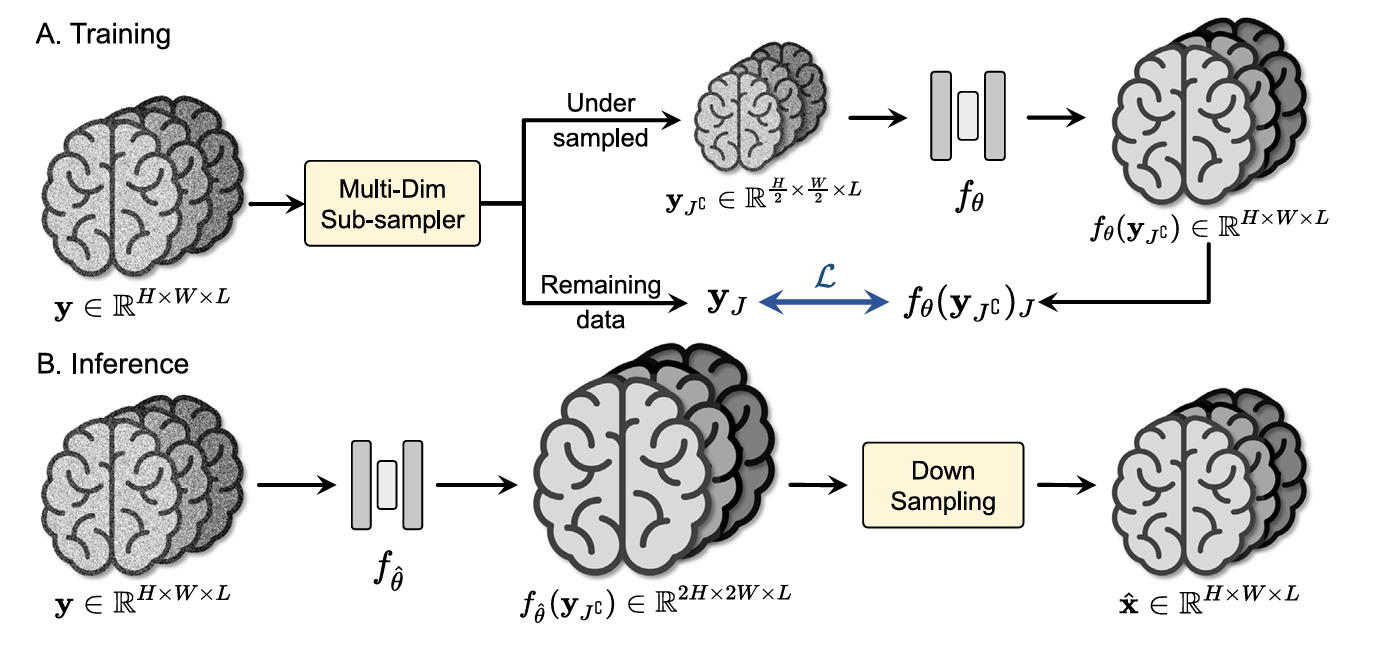 ×Self-supervised denoising for high-dimensional magnetic resonance imageBiomedical Signal Processing and Control 2025
×Self-supervised denoising for high-dimensional magnetic resonance imageBiomedical Signal Processing and Control 2025 - ICLR 2025
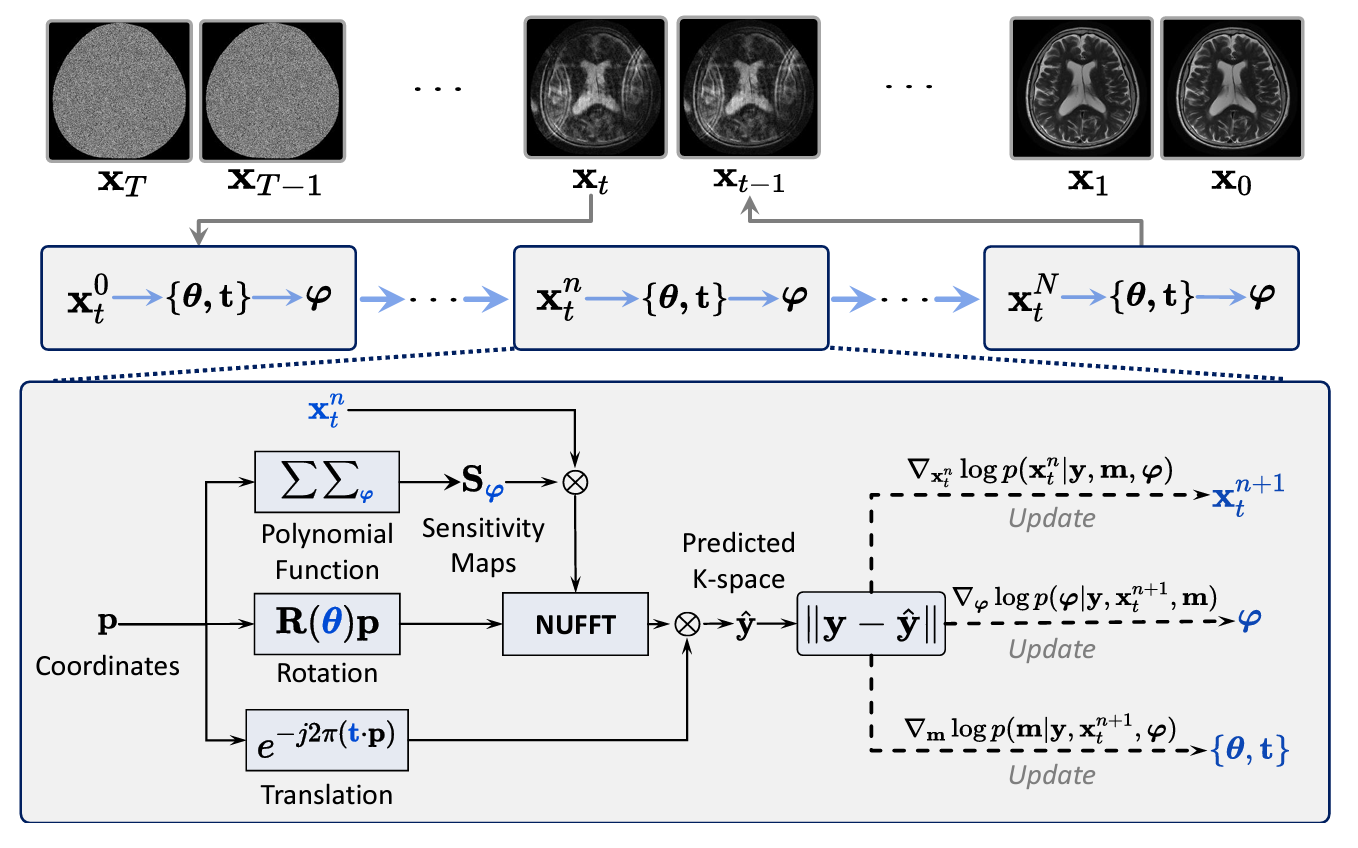
Spotlight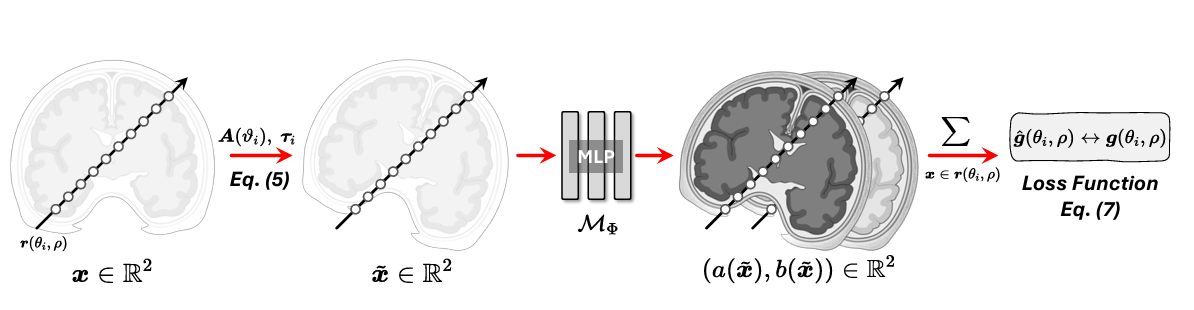 ×Moner: Motion Correction in Undersampled Radial MRI with Unsupervised Neural RepresentationThe 13th International Conference on Learning Representations 2025
×Moner: Motion Correction in Undersampled Radial MRI with Unsupervised Neural RepresentationThe 13th International Conference on Learning Representations 2025
2024
- MICCAI 2024
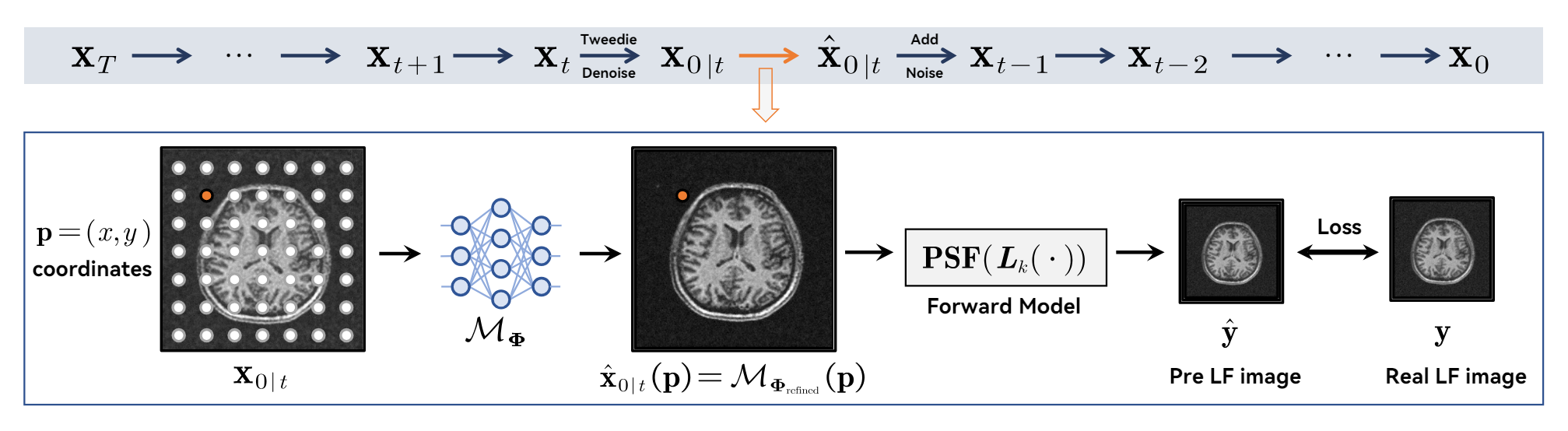 ×Zero-Shot Low-Field MRI Enhancement via Denoising Diffusion Driven Neural RepresentationInternational Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention 2024
×Zero-Shot Low-Field MRI Enhancement via Denoising Diffusion Driven Neural RepresentationInternational Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention 2024 - ISBI 2024
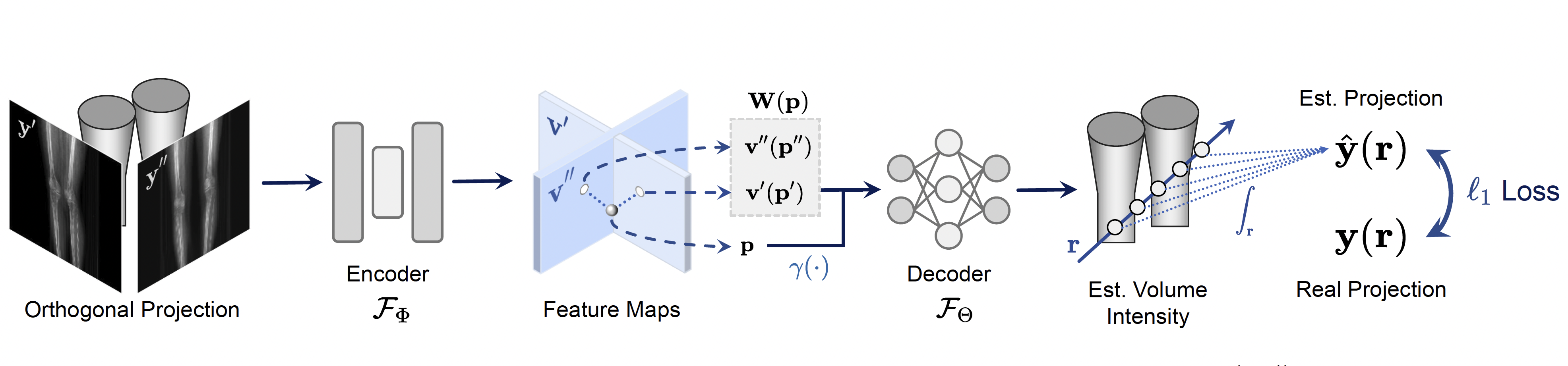 ×Reconstructing Knee CT Volumes from Biplanar X-Rays Via Self-Supervised Neural FieldIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2024
×Reconstructing Knee CT Volumes from Biplanar X-Rays Via Self-Supervised Neural FieldIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2024
2023
- ISBI 2023
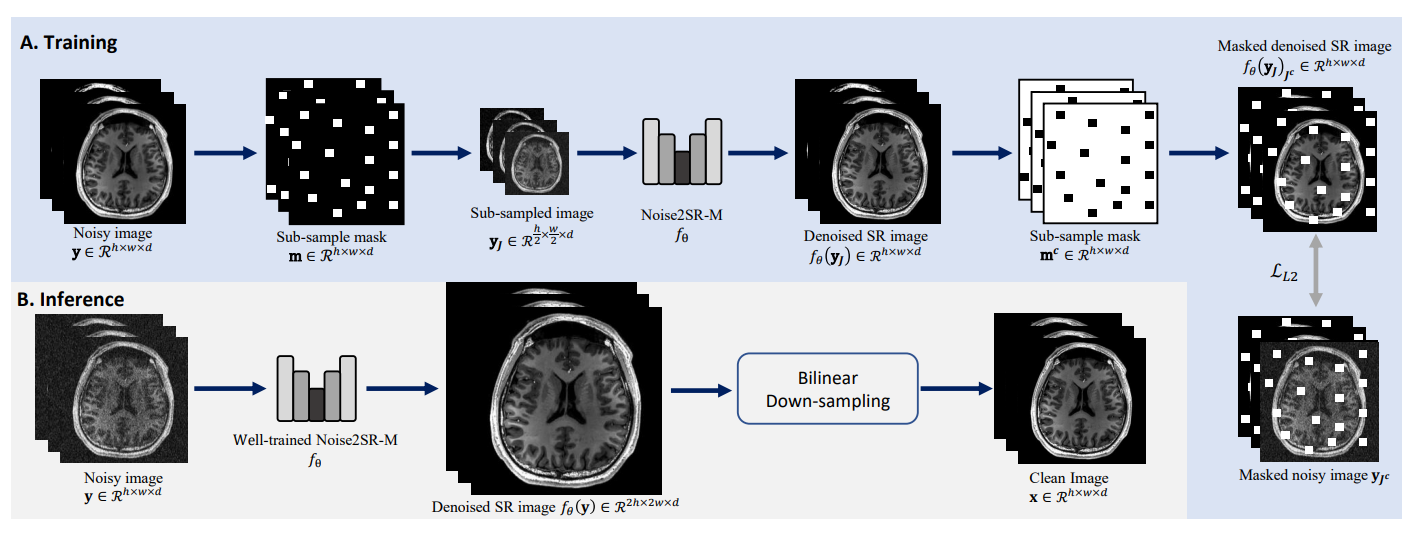 ×Self-supervised High-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Image Denoising Using Super-resolved Single Noisy ImageIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2023
×Self-supervised High-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Image Denoising Using Super-resolved Single Noisy ImageIEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2023